消息来源:
TechNode
原文标题:
China’s PC gamers will exceed US population in 2023: report
原文地址:
https://technode.com/2019/05/15/chinas-pc-gamers-will-exceed-us-population-in-2023-report/
内容转述:
(声明:以下转述内容仅供参考,任何有争议之处都以原文为准。)
游戏研究公司 Niko Partners 发布的一份报告显示,在 2023 年的时候,中国将有大约 3.54 亿 PC 端在线游戏玩家,这一数字将超越美国的人口总数。去年(2018年),中国有大约 3.12 亿 PC 端在线游戏玩家,他们中四分之一的人曾在游戏中付费。在 2018 年,中国 PC 在线游戏中的游戏内购买业务的总收入达到了 15.21 亿美元,超过了该项收入中全球总数的二分之一,而且,预计 2019 年全年,这一数字将达到 16 亿美元。除了 PC 端在线游戏之外,这份报告还指出,中国移动端游戏用户数和付费收入已经超过了 PC 端在线游戏,而且在未来五年内,移动端游戏的增长速度也将超越 PC 端。根据这份报告的预测,到 2023 年,中国将拥有 7.28 亿手机游戏用户,这大约是中国人口总数的一半。一个事实是,中国有 95% 的游戏者都在玩手机游戏,这很大程度上是由于手机游戏市场几乎已经饱和导致的。手机游戏市场在中国也拥有很大比例的付费用户,在 2018 年,大约有 40% 的手机游戏用户是付费用户。在 2018 年,中国国内的手机游戏收入为 15.63 亿美元,尽管这一数字没有超过 PC 端的在线游戏,但是,根据预期,手机游戏的收入在未来五年内将增长 63% 并在 2023 年达到 25.5 亿美元。在手机游戏中,电子运动类的游戏将是增长速度最快的,预计到 2023 年的时候,手机电子运动类游戏的收入将是现在的两倍并达到 11.5 亿美元,而且将占据整个手机游戏市场 45% 的份额。由于中国的游戏审批流程的改变,2019 年我们将看到游戏的批准名称将从 2018 年的 8000 个下降到 5000 个。不过,受影响的批准名称通常是低质量的复制游戏,不会真正影响整个市场的收入。
作者: 荒原之梦
解决并分析 Firefox 浏览器近期(2019年5月4日)发生的插件被异常禁用的问题
操作环境
操作系统:Windows 10 中文家庭版 64 位
Firefox 版本:66.0.3 (64-bit) 英文国际版
问题说明
2019年5月4日,我发现我的 Firefox 浏览器显示插件的位置一个插件都没有了,如图 1:
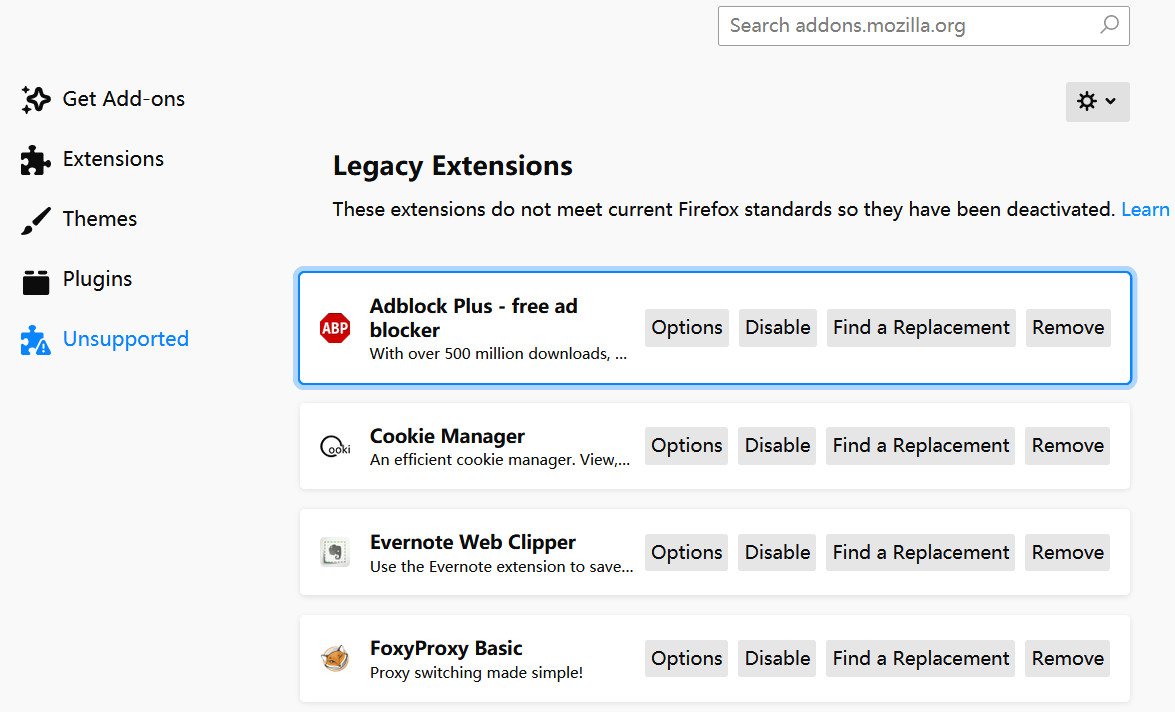
之后,打开 Firefox 的扩展页面 about:addons, 看到所有扩展都有了如下报错并被禁用,如图 2:
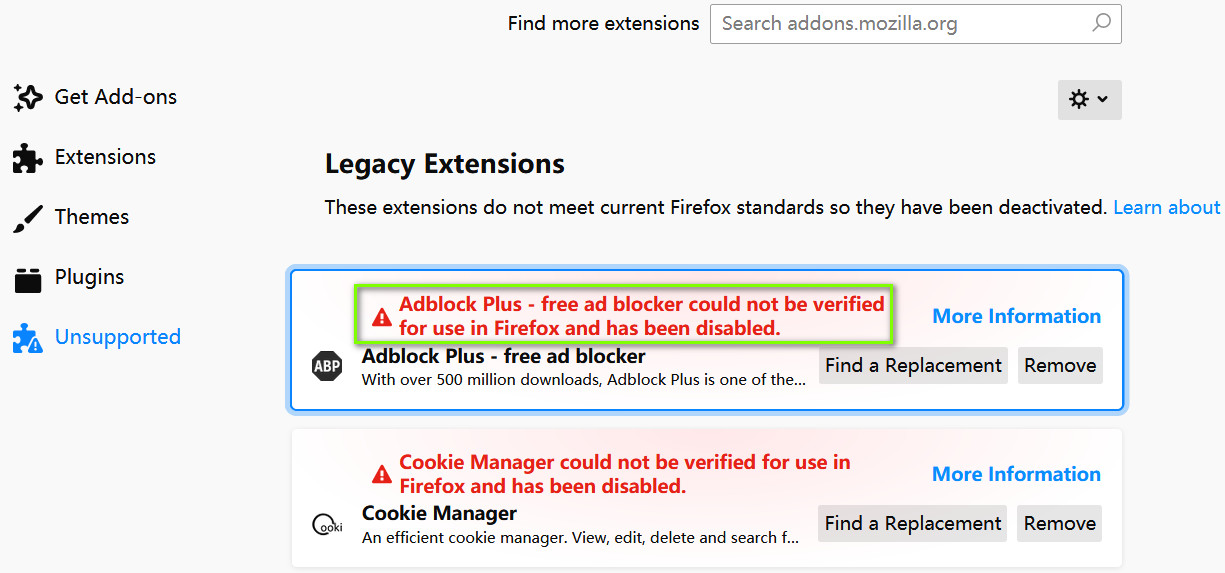
报错的文本内容如下:
XXX could not be verified for use in Firefox and has been disabled.
随后,我在“火狐社区(mozilla.com.cn)”中找到了对这个问题的说明和解决方案:
http://mozilla.com.cn/thread-413298-1-1.html
火狐社区对该问题的解释是:
由于 AMO(Firefox 扩展中心)中间签名证书过期,导致 Firefox 认为这些扩展是未签名的,所以会被禁用。
http://mozilla.com.cn/thread-413298-1-1.html
解决过程
依次打开火狐的”Options / Privacy & Security / Firefox Data Collection and Use”, 地址:
about:preferences#privacy
勾选”Allow Firefox to install and run studies”.
之后,点击该选项后面的”View Firefox studies”可以查看 Firefox 曾经安装和正在安装的一些实验项目(地址:about:studies.), 如图 3:
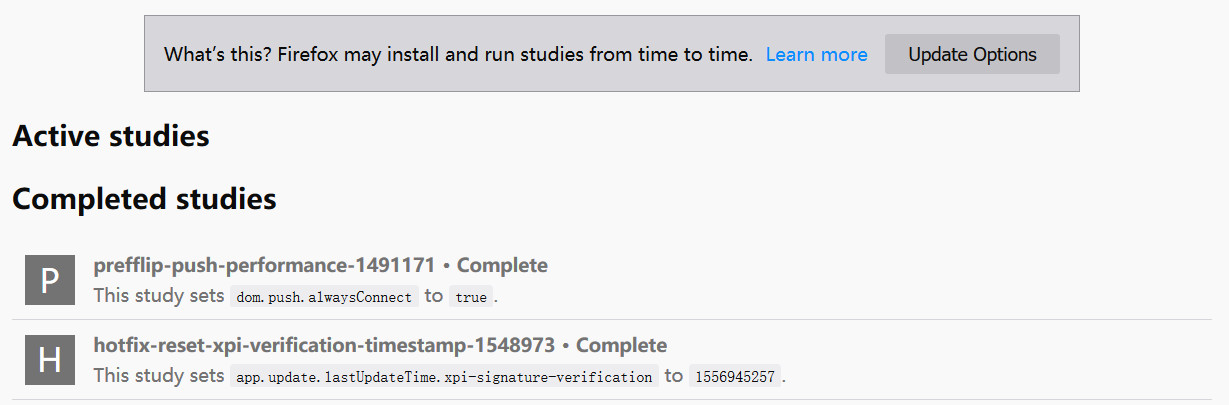
我的 about:studies 页面如图 4,但是,可以看到,在我进行了上面的操作之后,并没有和本次事件有关的实验项目的安装记录:
不过,在火狐社区该帖子(http://mozilla.com.cn/thread-413298-1-1.html)的下面的附件中给出了修复问题的扩展文件,可以手动下载之后拖到 Firefox 浏览器中安装,安装完成之后就恢复正常了,所有插件都可以正常使用了,如图 5 和 图 6:
问题分析
下载下来的扩展文件是后缀为 .xpi 的文件,全名如下:
hotfix-update-xpi-intermediate@mozilla.com-1.0.2-signed.xpi
使用 7-ZIP 对该文件解压后得到如下文件与文件夹(如图 7 所示):
在 META-INF 文件夹中包含如下三个文件:
- manifest.mf
- mozilla.rsa
- mozilla.sf
其中 mozilla.rsa 应该是和 Firefox 扩展中心的中间签名有关的文件了。在火狐社区中,Mozilla 员工 (ID: xuyuehang) 发表的回复中说明了 hotfix-update-xpi-intermediate@mozilla.com-1.0.2-signed.xpi 这个插件解决该问题的方式:
大约2小时前我们推送了部分修复:使用相同的名称/密钥生成了一个新的中间证书,但更新了有效时限,通过Firefox内置的热更新推送给用户,应该大多数用户会在未来几小时内看到扩展已恢复,已经有部分用户收到了更新
http://mozilla.com.cn/thread-413298-1-1.html
根据来自网络上的消息,自从 2016 年夏天的 FF48 后,正式版和 beta 版的 Firefox 安装的插件必须被 AMO 签名,Nightly 版和 Developer Edition 版可以加载未签名的插件,而这次问题发生的直接原因是 AMO 证书过期导致的。根据我查找到的资料,”AMO” 的全称应该是”Addons Mozilla Org”, 其网址为”https://addons.mozilla.org”.
MozillaWiki 上关于”AMO”的词条:https://wiki.mozilla.org/AMO
Firefox 官方对插件签名的说明:https://developer.mozilla.org/zh-CN/docs/Mozilla/Add-ons/Distribution
Firefox 官方对扩展和插件签名的说明:https://wiki.mozilla.org/Add-ons/Extension_Signing
Linux 安全加固:在 CentOS 上修改 SSH Server 的默认监听端口 (Linux Security Reinforcement: Modify the Default Listening Port for SSH Server on CentOS)
操作说明
22 号端口是 SSH Server 的默认监听端口,当有人对我们位于公网上的服务器进行端口扫描的时候,极有可能发现这个端口并尝试恶意登陆我们服务器上的 SSH Server, 因此修改这个默认监听端口就很有必要。
操作环境
本文中我的操作是在一台远程 VPS 上进行的(我无法连接该 VPS 的本地 Shell, 因此,在接下来的操作中我始终要确保能够远程登陆这台 VPS.), 其操作系统版本信息如下:
[root@GreedyIronclad-VM ~]# cat /etc/issue CentOS release 6.3 (Final) Kernel \r on an \m
操作步骤
打开 SSH Server 的配置文件:
vim /etc/ssh/sshd_config
可以找到如下内容:
#Port 22 #AddressFamily any #ListenAddress 0.0.0.0 #ListenAddress ::
去掉 “Port 22”[1] 前面的注释并在其下添加 “Port XXX”[2], 例如:
Port 22 Port XXX #AddressFamily any #ListenAddress 0.0.0.0 #ListenAddress ::
Restart SSH Server:
[root@GreedyIronclad-VM ~]# service sshd restart Stopping sshd: [ OK ] Starting sshd: [ OK ]
之后我们还需要对防火墙做一些设置,这样才能确保新增的监听端口 XXX[2] 不被防火墙阻断。
(在这里,有些文章可能建议大家直接关闭防火墙,我建议大家千万不要这么做。直接关闭防火墙确实可以省下很多麻烦,但是我们修改 SSH Server 的默认端口的目的就是为了增强服务器的安全性,如果为此而关闭了防火墙那岂不是得不偿失。)
具体操作如下:
编辑防火墙配置文件:
vim /etc/sysconfig/iptables
将用于 SSH Server 的 “XXX”[2] 端口加入允许规则:
-A INPUT -m state --state NEW -m tcp -p tcp --dport XXX -j ACCEPT
命令参数注释:
-A: 附加该规则到已有规则的末尾;
INPUT: 入站规则;
-m: 显示扩展;
-m state: 使用 state 扩展模块。当连接与跟踪结合使用时,state 模块允许访问数据包的连接跟踪状态;
-m state –state NEW: 连接中的第一个数据包;
-m tcp: 使用 TCP 扩展模块;
-p tcp: 指定待检查包的协议为 TCP 协议;
–dport XXX: 指定目的端口为 XXX;
-j ACCEPT: 如果数据包和该规则匹配则接受该数据包。
重启防火墙以使配置生效:
service iptables restart
之后,使用新增的非默认端口尝试连接远程服务器,如果可以连接成功(正常情况下,此时使用 22 号端口以及新增的非默认端口都可以连接远程服务器),则接下来我们就把原来的 22 端口禁用掉。
在 SSH Server 的配置文件中注释掉对 22 号端口的监听,编辑配置文件:
vim /etc/ssh/sshd_config
修改后如下:
#Port 22 Port XXX #AddressFamily any #ListenAddress 0.0.0.0 #ListenAddress ::
Restart SSH Server:
service sshd restart
此时,再次尝试连接 SSH Server 的 22 号端口应该就已经会被拒绝连接。但是为了更加安全,我们还需要在防火墙上拒绝入站请求 22 端口的连接。
在防火墙上禁止来自 22 端口的连接请求,编辑防火墙配置文件:
vim /etc/sysconfig/iptables
修改示例如下:
#-A INPUT -m state --state NEW -m tcp -p tcp --dport 22 -j ACCEPT -A INPUT -m state --state NEW -m tcp -p tcp --dport 22 -j DROP
Restart Iptables:
service iptables restart
注释
[1] 这一步不能去掉对原来的 22 号端口的监听,因为我们在修改配置文件时使用的还是 22 端口,一旦 22 端口失效而新增的监听端口没能正常工作,那么我们就失去了和远程服务器的连接。
[2] “XXX” 为你想要设置的 SSH Server 监听的端口号,建议应大于 10000, 因为如果攻击者从小到大依次扫描各个端口号,那么大于 10000 的端口被扫描到的可能性将大大降低。
关于近期发生的2017年10月和12月以及2018年01月和02月的部分文章图片失效事件的说明
近日,有读者来信告诉我,我有一篇文章里面的图片都无法显示了(在此,再次感谢这位热心的读者朋友 🙂 希望大家发现我网站里有什么错误和问题都向我指出来,我一定及时改正 🙂),随后我检查了那篇文章,发现 2017 年 10 月和 12 月以及 2018 年 01 月和 02 月的部分文章图片失效,共涉及 13 篇文章中的共计 160 张图片。
这些图片之所以失效,是因为我当时是把这些图片存储在了一家云服务提供商的对象存储容器中但是却没有在该容器上绑定我自己的域名,而是使用的服务商提供的他们自己的域名作为图片的链接地址插入到了博客文章中(我当时没有意识到绑定自己的域名的重要性,就这么直接用了),但是后来,这家云服务商更改了存储容器中用到的域名导致图片的链接地址发生了变化,于是,我网站中使用了原来的链接地址插入的图片就全都无法显示了。
虽然链接地址变了,但是图片都还在,因此,我把所有受影响的图片都转移到了另一个已经绑定了我自己的域名的存储容器中并更新了受到影响的文章中的图片的链接地址。
GitHub 部分仓库遭遇黑客攻击 (2019年5月)
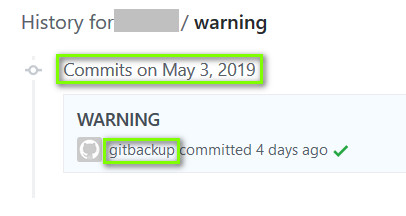
2019年5月3日[1],GitHub 上多个仓库的代码和提交记录被黑客删除并被替换成一个名为 “warning” 的文件,文件中的内容为:
To recover your lost code and avoid leaking it: Send us 0.1 Bitcoin (BTC) to our Bitcoin address 1ES14c7qLb5CYhLMUekctxLgc1FV2Ti9DA and contact us by Email at admin@gitsbackup.com with your Git login and a Proof of Payment. If you are unsure if we have your data, contact us and we will send you a proof. Your code is downloaded and backed up on our servers. If we dont receive your payment in the next 10 Days, we will make your code public or use them otherwise
GitHub.com
中文参考译文如下:
为了恢复你丢失的代码并且不想这些代码被泄露:向我们的比特币地址 “1ES14c7qLb5CYhLMUekctxLgc1FV2Ti9DA” 发送 0.1 个比特币,之后把你的 Git 仓库登陆凭证和付款证明发送到 “admin@gitsbackup.com” 这个电子邮箱。如果你不确定我们是否有你的数据,你可以联系我们,我们会给你发送一个证明。你的代码已经被下载并备份在我们的服务器上。如果我们在接下来的 10 天内没有收到你的付款,我们会公开你的代码并把它们用在其他地方。
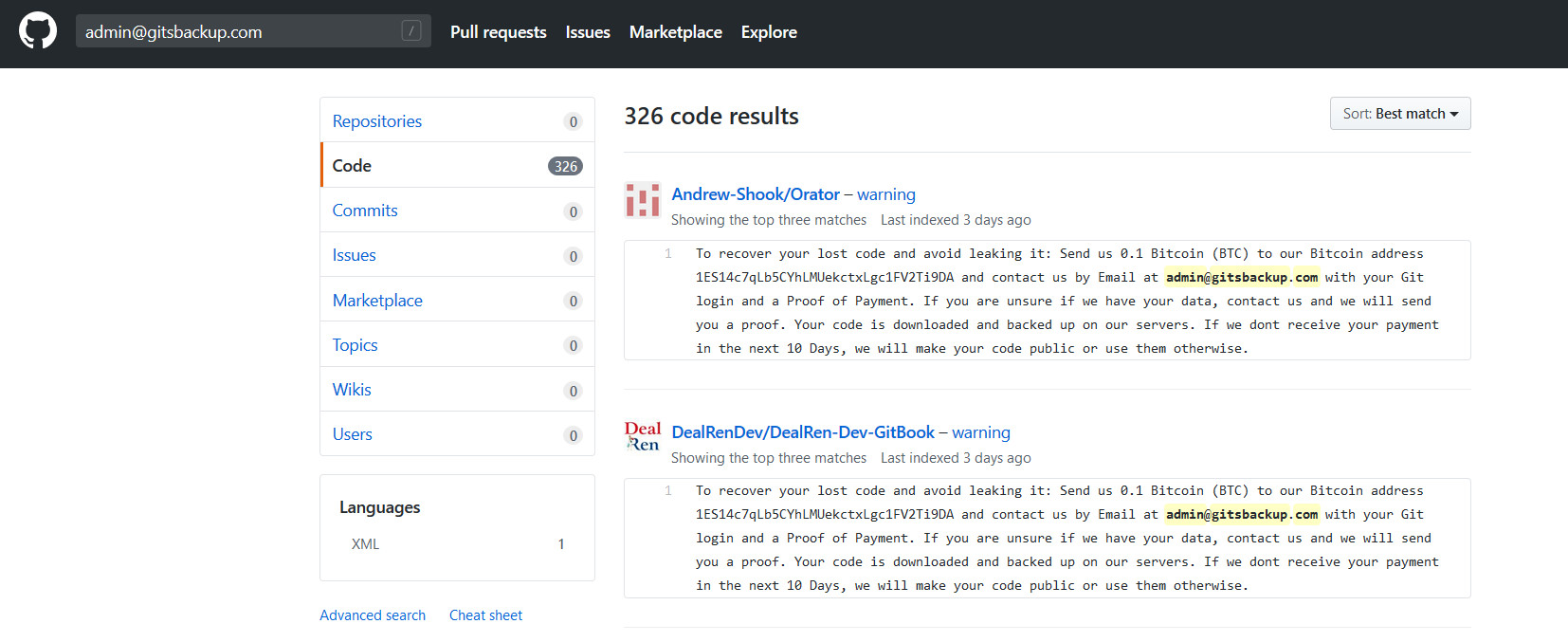
在 GitHub 中搜索 “admin@gitsbackup.com” 获得的搜索结果[2], 如图 1
除了 GitHub 之外,GitLab 和 Bitbucket 上的部分仓库也遭遇了可以认为与此一致的攻击。
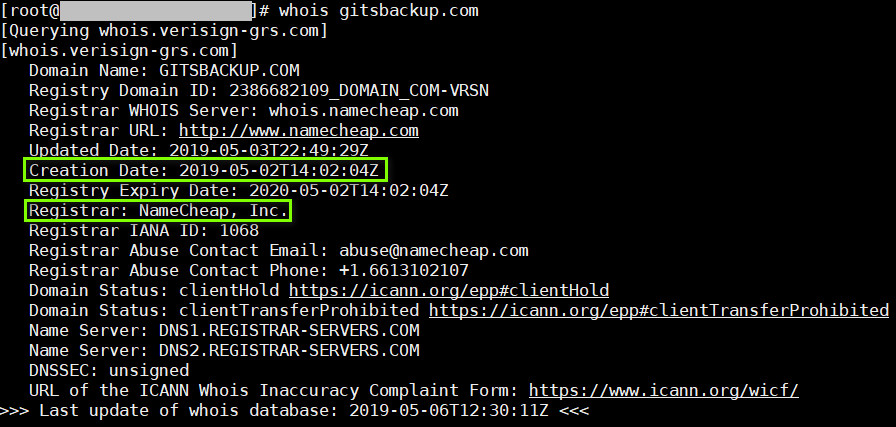
通过对”gitsbackup.com”这个域名的 whois 查询可以获知,该域名创建于 2019 年 5 月 2 日,注册商是 “NameCheap, Inc.”, 如图 2:
虽然黑客说可以向 “admin@gitsbackup.com” 这个邮箱地址发邮件,但是我通过 DIG 命令查找发现,无法获知 “gitsbackup.com” 这个域名的 MX 记录和 A 记录:
[root@***]# dig gitsbackup.com MX ; <<>> DiG 9.8.2rc1-RedHat-9.8.2-0.10.rc1.el6 <<>> gitsbackup.com MX ;; global options: +cmd ;; Got answer: ;; ->>HEADER<<- opcode: QUERY, status: NXDOMAIN, id: 21987 ;; flags: qr rd ra; QUERY: 1, ANSWER: 0, AUTHORITY: 1, ADDITIONAL: 0 ;; QUESTION SECTION: ;gitsbackup.com. IN MX ;; AUTHORITY SECTION: com. 899 IN SOA a.gtld-servers.net. nstld.verisign-grs.com. 1557146567 1800 900 604800 86400 ;; Query time: 35 msec ;; SERVER: 8.8.8.8#53(8.8.8.8) ;; WHEN: Mon May 6 08:40:18 2019 ;; MSG SIZE rcvd: 105 [root@***]# dig gitsbackup.com A ; <<>> DiG 9.8.2rc1-RedHat-9.8.2-0.10.rc1.el6 <<>> gitsbackup.com A ;; global options: +cmd ;; Got answer: ;; ->>HEADER<<- opcode: QUERY, status: NXDOMAIN, id: 18787 ;; flags: qr rd ra; QUERY: 1, ANSWER: 0, AUTHORITY: 1, ADDITIONAL: 0 ;; QUESTION SECTION: ;gitsbackup.com. IN A ;; AUTHORITY SECTION: com. 63 IN SOA a.gtld-servers.net. nstld.verisign-grs.com. 1557145722 1800 900 604800 86400 ;; Query time: 25 msec ;; SERVER: 8.8.8.8#53(8.8.8.8) ;; WHEN: Mon May 6 08:40:24 2019 ;; MSG SIZE rcvd: 105 [root@***]#
截至到 (UTC+08:00) 时区 2019 年 5 月 6 日 20 时 58 分,在 “www.blockchain.com” 这个网站上查询 “1ES14c7qLb5CYhLMUekctxLgc1FV2Ti9DA” 这个比特币钱包的交易记录发现,应该还没有人向该钱包地址支付 0.1 个比特币,如图 3:
(查看地址:https://www.blockchain.com/btc/address/1ES14c7qLb5CYhLMUekctxLgc1FV2Ti9DA)
注:
[1]该时间为 GitHub 上记录的黑客 push “warning” 文件的时间, 如图 4:
[2]该搜索结果不代表被黑的仓库总数。
汉语拼音 – 韦氏拼音对照表
韦氏拼音全名为 ”威妥玛式拼音法 (Wade-Giles romanization)” 又称 “威妥玛 – 翟理斯式拼音”.
韦氏拼音由英国人威妥玛 (Thomas Francis Wade) 等人于 1867 年开始编制. 韦氏拼音没有汉语拼音中用于表示声调的符号, 更加符合英文的表达习惯, 此外, 在韦氏拼音中使用送气符号 (‘) 来表示送气的声母. 中国大陆自 1958 年起开始推广汉语拼音, 但是韦氏拼音在西方学术界以及一些和中国有关的英文单词, 人名, 地名, 商标名等中仍有使用.
(以下 ”汉语拼音 – 韦氏拼音对照表” 中的数据整理自网络, 仅供参考.)
继续阅读“汉语拼音 – 韦氏拼音对照表”“Health” and “Wealth”
Health is wealth.
1
Health: n.健康
Wealth: n.财富
e.g.1
His wife Cheryl said she had no worries about his health.
他的妻子谢里尔说她并不担心他的健康.
e.g.2
Economic reform has brought relative wealth to peasant farmers.
经济改革给农民带来了相对的财富.
2
Healthy adj.健康的; 大量的; 有益于健康的
Wealthy adj.富有的
e.g.1
You can’t do anything without a healthy body.
没有健康的身体你什么也没有.
e.g.2
The birth of a live healthy body is a truly blessed event.
一个健康活泼的婴儿的出生真是一件可喜的事.
e.g.3
It had once been the home of a wealthy nobleman.
这里曾经是一个富有贵族的官邸.
e.g.4
Soon, members of the Royal family and other wealthy people took up motoring as a sport.
很快, 皇室成员们和其他富有的人们都把驾驶汽车当作了一种乐趣.
e.g.5
They live in a wealthy suburb of Chicago
他们住在芝加哥郊区的一处富人区.
e.g.6
A wealthy nation.
一个富饶的国度.
3
Healthier adj.健康的, 有益于健康的(healthy 的比较级)
Wealthier adj.富有的(wealthy 的比较级)
e.g.1
Workplace canteens are offering healthier foods than ever before.
单位餐厅以前从没有提供过像现在这样健康的饭菜.
e.g.2
They’ve got to force people to get healthier.
他们必须强迫人们变得更加健康.
e.g.3
Japan is wealthier and more powerful than ever before.
日本比以往任何时候都更加富有和强大.
4
Healthiest adj.健康的, 有益于健康的(healthy 的最高级)
Wealthiest adj.富有的(wealthy 的最高级)
e.g.1
On paper, I am the healthiest man alive, yet I feel permanently unwell.
理论上讲, 我是或者的最健康的人, 但是我总感觉不舒服.
e.g.2
The very wealthiest men and women are suffering too.
最富有的人也在受苦.
5
Healthily adv.健康地
e.g.1
I was eating normally and healthily and doing the right exercise.
我的饮食很正常和健康, 并且我也会做一些恰当的运动.
e.g.2
I had never seen bombing on such a scale, and I was healthily apprehensive.
我从没见过如此大规模的轰炸, 所以我的恐惧是理所当然的.
解决 CentOS 7 报错: /var/run/yum.pid 已被锁定
报错描述
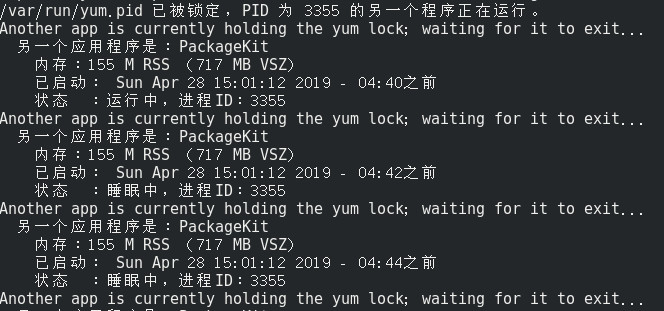
今天在使 yum 命令安装软件的时候遇到了如下报错:
/var/run/yum.pid 已被锁定,PID 为 3355 的另一个程序正在运行。
Another app is currently holding the yum lock; waiting for it to exit...
另一个应用程序是:PackageKit
内存:155 M RSS (717 MB VSZ)
已启动: Sun Apr 28 15:01:12 2019 - 04:40之前
状态 :运行中,进程ID:3355
报错截图如下:
解决方案
运行下面的命令, 强制结束 yum 进程即可:
rm -f /var/run/yum.pid
另外, 如果担心强制删除系统文件会引发难以预测的错误, 也可以尝试稍等一会(经过实测发现, 稍微等待一段时间后上述报错可能会自行消失)或者选择重启系统.
解决 CentOS 7 报错: “Repository base is listed more than once in the configuration”和”没有可用软件包 XXX”的问题
报错描述
我的 CentOS 7 的更新源使用的是直接从 163 镜像站上下载的更新源文件.
今天在使用 yum makecache 命令从更新服务器上把软件包的信息下载到本地缓存起来时遇到了如下报错:
Repository base is listed more than once in the configuration Repository updates is listed more than once in the configuration Repository extras is listed more than once in the configuration Repository centosplus is listed more than once in the configuration
报错截图如下:
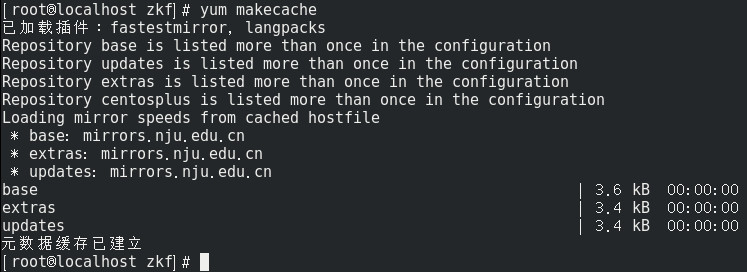
而且在我使用 yum install htop 命令安装 htop 的时候, 还提示:
没有可用软件包 htop。
错误:无须任何处理
但是, 正常情况下 CentOS 7 的源里面应该是有 htop 这个软件包的, 可以直接使用 yum install htop 成功安装(我之前安装过).
上述问题的相关截图如下:
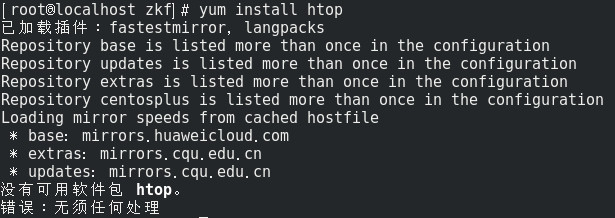
解决方案
分析上面的报错, 主要还是软件源文件出了问题, 于是我们先进入软件源配置文件所在的目录下:
cd /etc/yum.repos.d/
ls 查看一下, 回显如下:
[root@localhost yum.repos.d]# ls CentOS7-Base-163.repo CentOS-CR.repo CentOS-Media.repo CentOS-Base.repo CentOS-Debuginfo.repo CentOS-Sources.repo CentOS-Base.repo.backup CentOS-fasttrack.repo CentOS-Vault.repo [root@localhost yum.repos.d]#
从对报错内容的分析来看, 应该是软件源有重复(“listed more than once”), 所以这里我们尝试删除一些上面的软件源配置文件.
在删除之前, 先对 /etc/yum.repos.d/ 目录下的文件做一个整体的备份, 以便于尝试失败后的还原, 操作过程如下:
将 /etc/yum.repos.d/ 目录下的文件整体压缩成一个 .zip 文件:
zip centos7-repo.zip /etc/yum.repos.d/*
然后执行删除操作:
rm -rf CentOS-CR.repo CentOS-Debuginfo.repo CentOS-fasttrack.repo CentOS-Media.repo CentOS-Sources.repo CentOS-Vault.repo
之后把 CentOS7-Base-163.repo 中的内容复制进 CentOS-Base.repo:
cp -p CentOS7-Base-163.repo CentOS-Base.repo
最后删除 CentOS7-Base-163.repo:
rm -rf CentOS7-Base-163.repo
之后运行如下命令重建缓存, 没有再出现”Repository base is listed more than once in the configuration”的报错:
yum clean all yum makecache
但是, 在我尝试使用 yum 命令安装软件时, 仍然遇到了”没有可用软件包 XXX”的报错, 如下:
[root@localhost yum.repos.d]# yum install htop 已加载插件:fastestmirror, langpacks Loading mirror speeds from cached hostfile 没有可用软件包 htop。 错误:无须任何处理
“没有可用软件包”说明在 YUM 源中没有对应的软件包(163 的源本身应该是没有问题的, 这是一个大家都常使用的 Linux 方面的国内软件源).
其实, 在 CentOS 和 RHEL 等操作系统中, 常使用的软件源不仅有 YUM, 还有 EPEL. EPEL 英文全称为:”Extra Packages for Enterprise Linux”. 直译为中文就是”用于企业 Linux 的额外软件包”. EPEL 是 Fedora 的一个项目, 有关该项目的官方说明可以在下面的链接中找到:
这里我摘录一段 Fedora 对 EPEL 项目的说明:
企业版 Linux 附加软件包(以下简称 EPEL)是一个 Fedora 特别兴趣小组,用以创建、维护以及管理针对企业版 Linux 的一个高质量附加软件包集,面向的对象包括但不限于 红帽企业版 Linux (RHEL)、 CentOS、Scientific Linux (SL)、Oracle Linux (OL) 。
EPEL 的软件包通常不会与企业版 Linux 官方源中的软件包发生冲突,或者互相替换文件。EPEL 项目与 Fedora 基本一致,包含完整的构建系统、升级管理器、镜像管理器等等。
https://fedoraproject.org/wiki/EPEL/zh-cn
在 CentOS 7 中安装 EPEL 源的命令如下:
yum install -y epel-release
安装完成后, 在 /etc/yum.repos.d 目录下会多出来下面两个文件, 这两个文件就是 EPEL 源的配置文件:
- epel.repo
- epel-testing.repo
查看 epel.repo 文件中的内容可以发现其中软件源的地址指向的是 https://mirrors.fedoraproject.org/, epel-testing.repo 这个文件中的软件源的地址也是指向的是 https://mirrors.fedoraproject.org/. 为了加快软件安装速度, 我们可以将其更改为国内的 EPEL 源, 操作步骤如下:
进入 /etc/yum.repos.d 目录, 下载阿里云 EPEL 源:
wget http://mirrors.aliyun.com/repo/epel-7.repo
备份 Fedora 官方提供的 EPEL 源配置文件:
cp -p epel.repo epel.repo.bak cp -p epel-testing.repo epel-testing.repo.bak
删除 epel-testing.repo:
rm -rf epel-testing.repo
将 epel-7.repo 中的内容覆盖写入到原来的 epel.repo 文件中:
cp -p epel-7.repo epel.repo
删除 epel-7.repo 文件:
rm -rf epel-7.repo
重新生成缓存:
yum clean all yum makecache
之后可以正常安装软件.
总结
遇到”Repository base is listed more than once in the configuration”的问题要考虑系统中是否存在重复的软件源, 遇到”没有可用软件包 XXX”的问题首先要确认要安装的软件包名称是否写对了, 例如安装 pip 的命令不是 yum install pip, 而是 yum install python-pip, 在此之后如果问题仍然存在就需要考虑当前系统中是否正确配置了 YUM 和 EPEL 两个软件源.
百度浏览器宣布 PC 端部分功能停止服务
百度浏览器于 2019 年 04 月 03 日发布公告称将于 2019 年 04 月 30 日对产品部分功能停止服务, 停止服务的产品包括桌面百度, 百度工具栏, 百度地址栏, 百度极速浏览器和 hao123 浏览器. 这些停止服务的产品将不再更新.
公告全文如下:
【公告】百度浏览器(PC)部分功能停止服务
尊敬的用户:
您好,由于部门业务调整,官方将于2019年04月30日对产品部分功能停止服务。相关的产品包括桌面百度、百度工具栏、百度地址栏、百度极速浏览器,hao123浏览器,产品将不再更新,基本功能本地仍可使用。相关事宜公告如下:
1、用户登录功能,已登录用户登录状态失效,但仍可本地保留用户基本信息(收藏夹、历史纪录、设置等),未登录用户将不提供服务;
2、积分商城将无法访问,不提供用户积分查询服务;
3、用户的设置信息、历史纪录、收藏夹云同步失效;
4、产品相关推荐内容消失,相关页面将不能访问,如:新建标签(newtab.baidu.com)、主页(0.baidu.com);
5、一切插件相关功能均不可用,已经安装插件的可能部分能够继续使用;
6、皮肤相关将保留简单样式,其它不可用;
由此带来的不便敬请谅解。感谢您的理解与支持!我们衷心期待您的继续支持和关注百度旗下更多优秀的产品!2019年04月03日
来自: https://gss0.bdstatic.com/5bVWsj_p_tVS5dKfpU_Y_D3/res/notice_llq.html
公告截图如下:
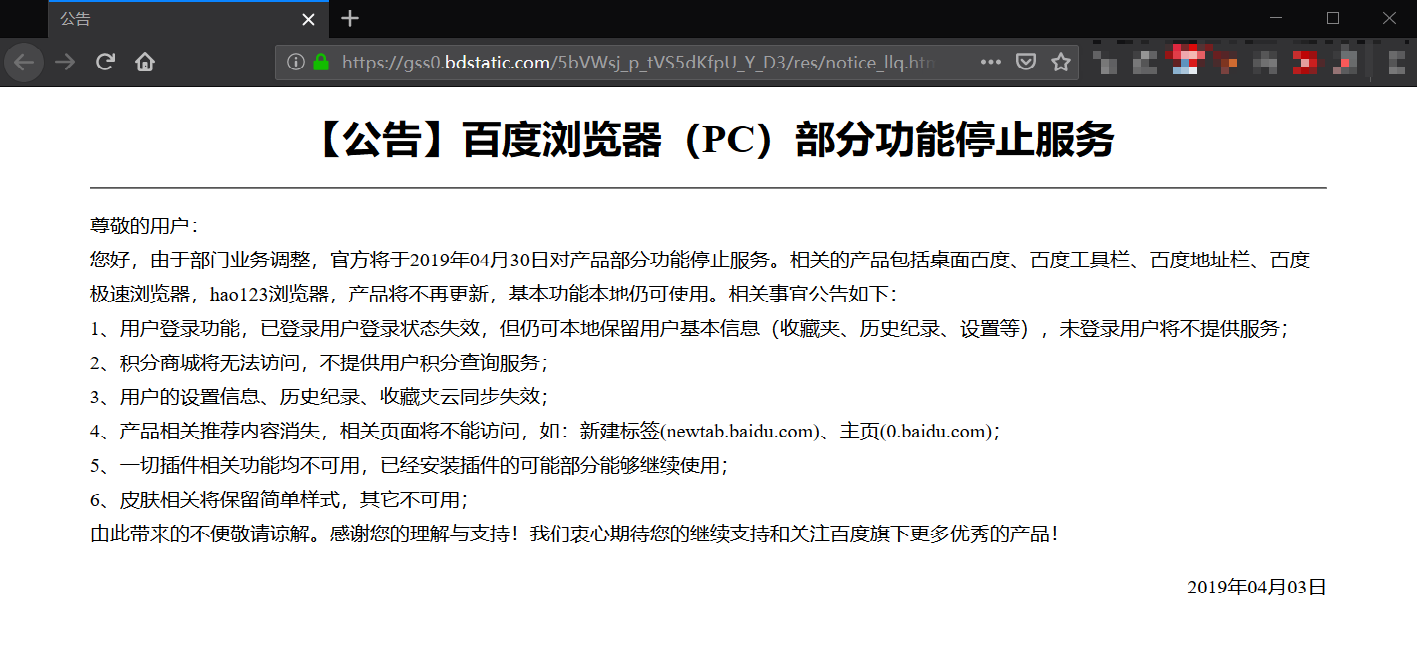
目前输入百度浏览器的官网地址”https://liulanqi.baidu.com/”会跳转到”https://gss0.bdstatic.com/5bVWsj_p_tVS5dKfpU_Y_D3/res/notice_llq.html”并显示上述关于百度浏览器停止服务的公告.
“https://liulanqi.baidu.com/”到”https://gss0.bdstatic.com/5bVWsj_p_tVS5dKfpU_Y_D3/res/notice_llq.html”的跳转过程是使用 302 暂时性转移重定向实现的, 如图 2:
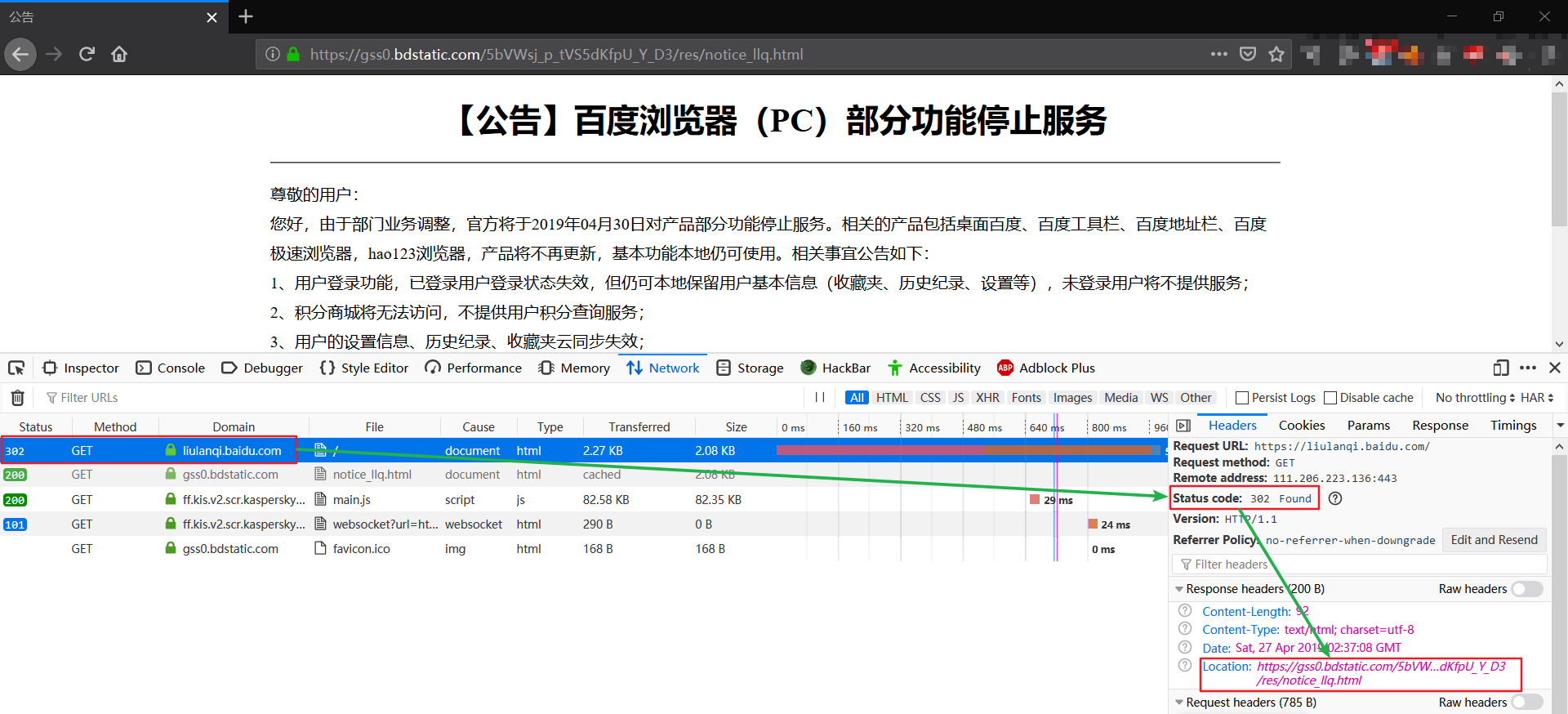
“gss0.bdstatic.com”是百度 CDN 的一个节点域名, 备案号为”京ICP证030173号-23”.
Ubuntu 19.04 国内更新源
2019年4月18日, Ubuntu 19.04 正式发布. Ubuntu 19.04 的 Codename 是”disco(迪斯科舞厅)”:
zkf@ubuntu:~$ lsb_release -c Codename: disco
为了方便国内用户使用最新版的 Ubuntu 19.04, 本文提供了 Ubuntu 19.04 的国内更新源以及更改更新源的完整步骤.
进入更新源文件所在目录:
cd /etc/apt/
备份原有更新源文件:
sudo cp -p sources.list sources.list.bak
编辑更新源文件:
sudo vi sources.list
写入如下国内更新源:
#阿里云源 deb http://mirrors.aliyun.com/ubuntu/ disco main restricted universe multiverse deb-src http://mirrors.aliyun.com/ubuntu/ disco main restricted universe multiverse deb http://mirrors.aliyun.com/ubuntu/ disco-security main restricted universe multiverse deb-src http://mirrors.aliyun.com/ubuntu/ disco-security main restricted universe multiverse deb http://mirrors.aliyun.com/ubuntu/ disco-updates main restricted universe multiverse deb-src http://mirrors.aliyun.com/ubuntu/ disco-updates main restricted universe multiverse deb http://mirrors.aliyun.com/ubuntu/ disco-backports main restricted universe multiverse deb-src http://mirrors.aliyun.com/ubuntu/ disco-backports main restricted universe multiverse deb http://mirrors.aliyun.com/ubuntu/ disco-proposed main restricted universe multiverse deb-src http://mirrors.aliyun.com/ubuntu/ disco-proposed main restricted universe multiverse #中科大源 deb https://mirrors.ustc.edu.cn/ubuntu/ disco main restricted universe multiverse deb-src https://mirrors.ustc.edu.cn/ubuntu/ disco main restricted universe multiverse deb https://mirrors.ustc.edu.cn/ubuntu/ disco-updates main restricted universe multiverse deb-src https://mirrors.ustc.edu.cn/ubuntu/ disco-updates main restricted universe multiverse deb https://mirrors.ustc.edu.cn/ubuntu/ disco-backports main restricted universe multiverse deb-src https://mirrors.ustc.edu.cn/ubuntu/ disco-backports main restricted universe multiverse deb https://mirrors.ustc.edu.cn/ubuntu/ disco-security main restricted universe multiverse deb-src https://mirrors.ustc.edu.cn/ubuntu/ disco-security main restricted universe multiverse deb https://mirrors.ustc.edu.cn/ubuntu/ disco-proposed main restricted universe multiverse deb-src https://mirrors.ustc.edu.cn/ubuntu/ disco-proposed main restricted universe multiverse #163源 deb http://mirrors.163.com/ubuntu/ disco main restricted universe multiverse deb http://mirrors.163.com/ubuntu/ disco-security main restricted universe multiverse deb http://mirrors.163.com/ubuntu/ disco-updates main restricted universe multiverse deb http://mirrors.163.com/ubuntu/ disco-proposed main restricted universe multiverse deb http://mirrors.163.com/ubuntu/ disco-backports main restricted universe multiverse deb-src http://mirrors.163.com/ubuntu/ disco main restricted universe multiverse deb-src http://mirrors.163.com/ubuntu/ disco-security main restricted universe multiverse deb-src http://mirrors.163.com/ubuntu/ disco-updates main restricted universe multiverse deb-src http://mirrors.163.com/ubuntu/ disco-proposed main restricted universe multiverse deb-src http://mirrors.163.com/ubuntu/ disco-backports main restricted universe multiverse #清华源 deb https://mirrors.tuna.tsinghua.edu.cn/ubuntu/ disco main restricted universe multiverse deb-src https://mirrors.tuna.tsinghua.edu.cn/ubuntu/ disco main restricted universe multiverse deb https://mirrors.tuna.tsinghua.edu.cn/ubuntu/ disco-updates main restricted universe multiverse deb-src https://mirrors.tuna.tsinghua.edu.cn/ubuntu/ disco-updates main restricted universe multiverse deb https://mirrors.tuna.tsinghua.edu.cn/ubuntu/ disco-backports main restricted universe multiverse deb-src https://mirrors.tuna.tsinghua.edu.cn/ubuntu/ disco-backports main restricted universe multiverse deb https://mirrors.tuna.tsinghua.edu.cn/ubuntu/ disco-security main restricted universe multiverse deb-src https://mirrors.tuna.tsinghua.edu.cn/ubuntu/ disco-security main restricted universe multiverse deb https://mirrors.tuna.tsinghua.edu.cn/ubuntu/ disco-proposed main restricted universe multiverse deb-src https://mirrors.tuna.tsinghua.edu.cn/ubuntu/ disco-proposed main restricted universe multiverse
更新系统:
sudo apt-get update sudo apt-get upgrade
拟定每年的 4 月 18 日为本站的”数据安全日”
就在刚刚过去的 4 月 18 日的下午, 我在使用 “tar” 命令对网站的文件进行打包备份时, 由于将 “tar” 命令后面的参数写反了, 导致网站文件发生错误, Web 服务器也发生故障, 进而使本站无法访问. 由于我在故障发生之前备份了数据库, 再加上本站大部分图片都存储在独立的图片服务器中, 因此我才得以在 4 月 19 日的下午将网站恢复并上线.
这次网站事故使我深刻意识到数据安全的重要性, 如果我没有数据库的备份文件, 那么很可能导致我投入很多精力维护的这个网站就此消失, 因此, 我计划将每年的 4 月 18 日定为本站的 “数据安全日”, 即惊醒自己, 也希望大家都能更加重视数据安全.
另外, 关于本次网站事故的发生过程与我的处理过程, 我会在之后写一篇博文详细回顾.
巴黎圣母院大火:世界文明的又一次劫难
法国当地时间 4 月 16 日(周一),位于巴黎市中心的巴黎圣母院发生火灾。根据有关报道,本次火灾造成巴黎圣母院三分二的塔顶被毁,但好在整体结构得以保存。
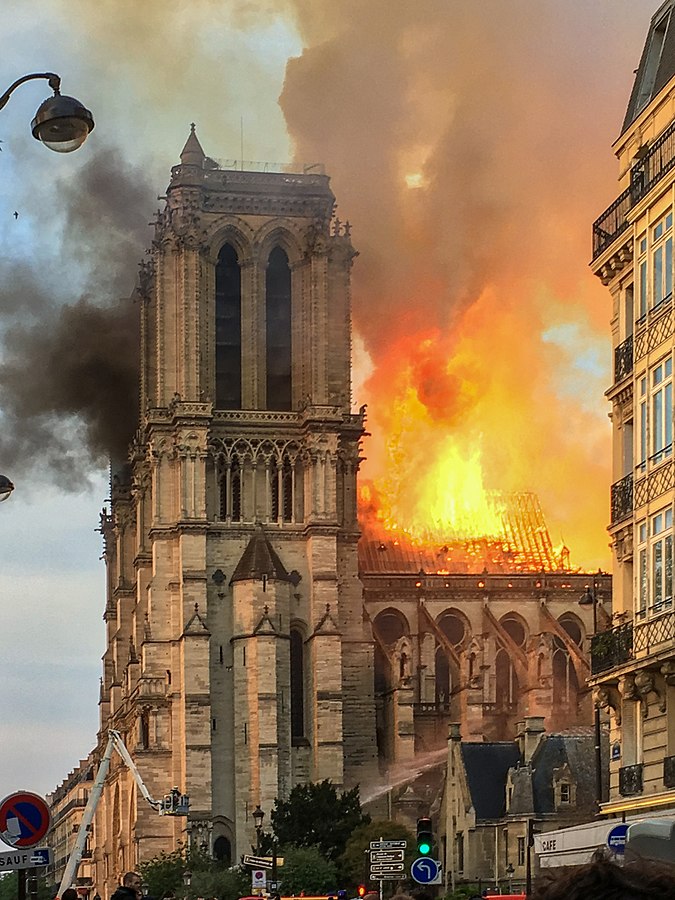

发生本次火灾之前的巴黎圣母院:

巴黎圣母院大约建造于 1163 年到 1250 年期间,全名为“巴黎圣母主教座堂 (Cathédrale Notre-Dame de Paris)”是一座哥特式建筑。
巴黎圣母院既是一座教堂,也是一个艺术品,例如在本次大火中被烧毁的尖塔和玫瑰花窗 (2019 年 4 月 17 日下午 16 时 10 分更新:据报道,法国官方确认三面玫瑰花窗均安全) 都具有极高的艺术价值。
巴黎圣母院的玫瑰花窗:

從蒙帕納斯大樓遠眺巴黎聖母院:
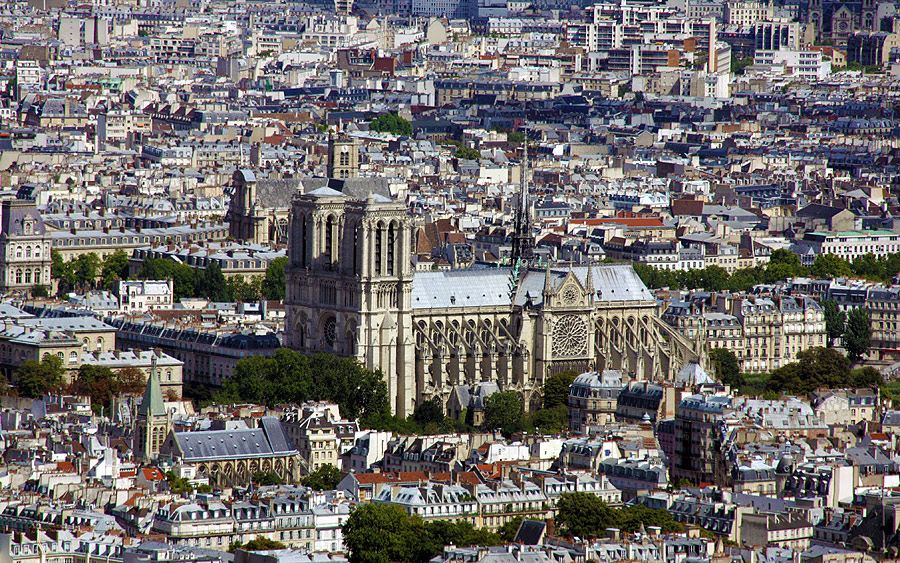

大火发生时,许多民众在塞纳河畔忍不住哭泣,还有人跪地祈祷。火灾发生当晚,一些人向着巴黎圣母院的方向合唱圣歌,寄托心中的悲痛。虽然巴黎圣母院不在中国,但是这种看着本国和本民族文明象征的珍宝被毁时的切肤之痛,中国人是有同感的。
巴黎圣母院还可以修缮重建,也许再过八百年之后,巴黎圣母院仍然是一座恢弘壮丽的建筑,继续向全世界慕名而来的游客讲述着法兰西文明的多姿多彩,但是,我们的圆明园却被永远地禁锢在一片废墟之中,千千万万生长在这片土地上的中国人再也没有可能去一睹这座园林的雄伟壮阔。是的,圆明园之所以被烧的一部分原因是当时的中国软弱无能,“落后就要挨打”是弱肉强食的历史铁律——直到今天仍然如此。
不过,我并不认同一部分人因为英法联军曾经火烧圆明园而对如今法国的遭遇落井下石,说这是“天道轮回”。
我们不能以一部分人在一段时间内的罪行作为衡量一个国家或民族的所有人在整个历史长河中的善恶。艺术和科学一样都是没有国界的,巴黎圣母院不仅仅是法国人的,也是全世界的,作为人类的一份子,我也不希望看到如同巴黎圣母院这样的人类文明的宝贵财富在烈火中毁于一旦,正如我同样不希望圆明园在烈火中毁于一旦一样。
中国的圆明园,法国的巴黎圣母院以及世界上其他国家和地区的珍贵文物都是人类先民的智慧结晶,代表着一个国家和民族的历史,也代表着人类文明。希望在未来,这样的文明劫难能够不再发生,无论是人类之间还是人类与人类文明之间,都需要相互爱护与包容。
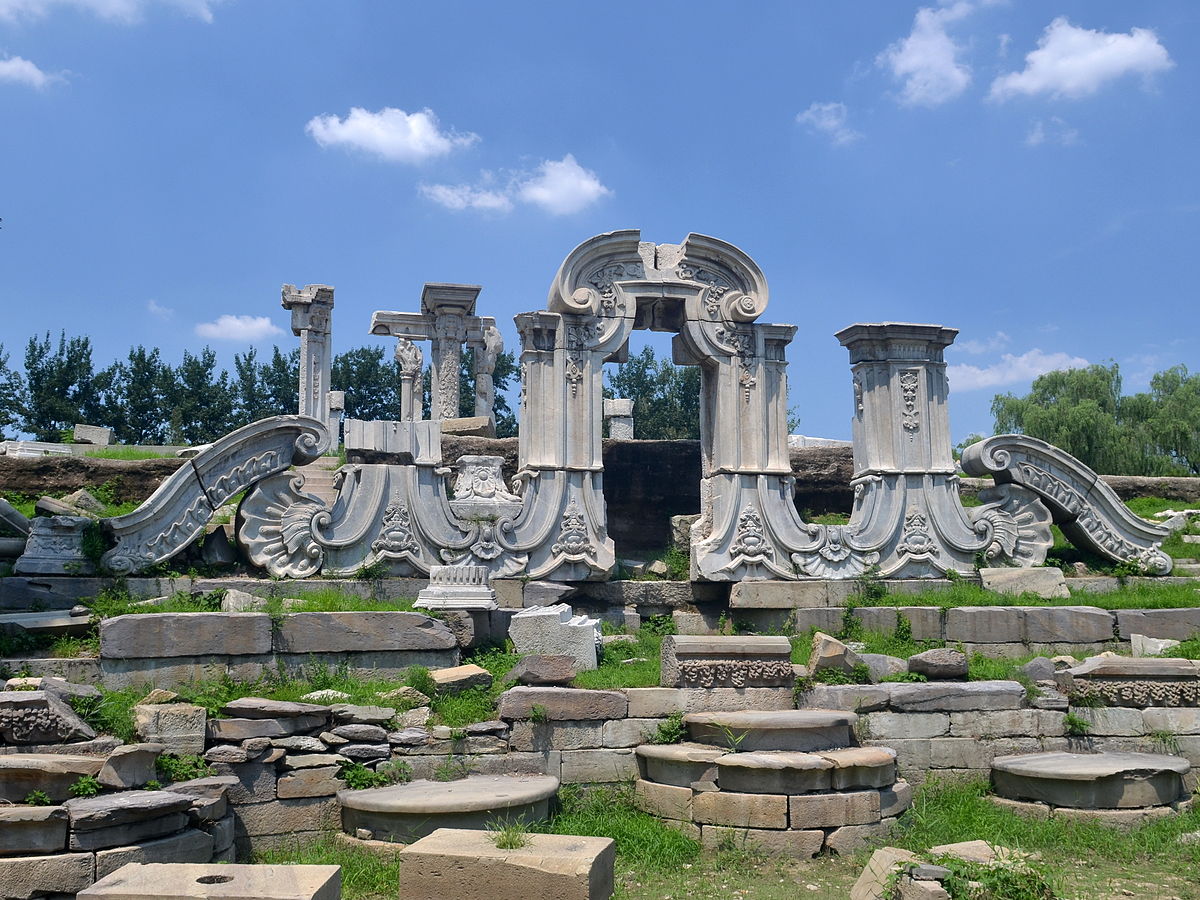
圆明园大水法残迹:

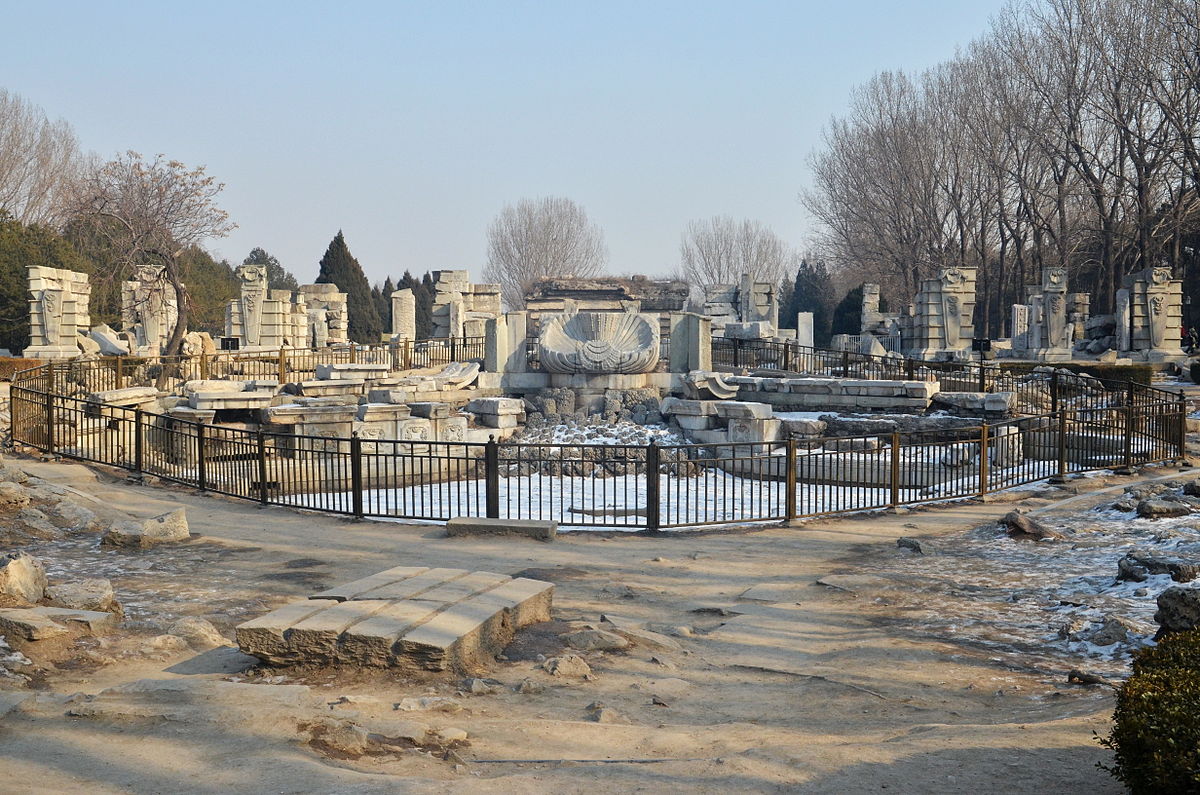
圆明园海晏堂遗址正面喷水池(十二生肖人身兽首像所在地):

降低 Kali Linux 资源占用:配置使用 Xfce 4 桌面环境
前言
Xfce Desktop Environment website:
https://www.xfce.org/
Xfce-维基百科:
https://zh.wikipedia.org/wiki/Xfce
Xfce 不是最华丽的 Linux 桌面环境,但却是相当节省系统资源的 Linux 桌面环境。就我个人的使用习惯而言,在 Linux 上,特别是 Linux 虚拟机中使用 Xfce 桌面是一个极佳的选择,因为这样可以把有限的系统资源更多地用于处理生产性作业。
Xfce 最新的版本是 “4.12”.
Kali Linux 2019.1 以及该版本之前的一些版本使用的都是 Gnome 桌面环境而不是 Xfce, 因此,本文就从降低系统资源占用的角度出发,介绍一下将 Kali 的桌面环境从 Gnome 更换到 Xfce 4 的过程。
过程
安装 Xfce 4,命令:
apt install kali-defaults kali-root-login desktop-base xfce4 xfce4-places-plugin xfce4-goodies
在安装的过程中(可能)会要求我们选择提供图形化系统登录界面的图形管理程序(A display manage is a program that provides graphical login for the X Windows System.),只有一个显示管理器可以管理给定的 X server (X server 是用于管理图形化界面的服务器端程序),但是如果当前系统中安装了多个显示管理器包,就需要选择一个默认的显示管理器(Only one display manage can manage a given X server, but multiple display manager packages are installed. Please select which display manager should run by default.),这里我选择的默认显示管理器是 “gdm3”, 如图 1:
切换桌面:
update-alternatives --config x-session-manager
回显如下:
root@kali:~# update-alternatives --config x-session-manager There are 3 choices for the alternative x-session-manager (providing /usr/bin/x-session-manager). Selection Path Priority Status ------------------------------------------------------------ * 0 /usr/bin/gnome-session 50 auto mode 1 /usr/bin/gnome-session 50 manual mode 2 /usr/bin/startxfce4 50 manual mode 3 /usr/bin/xfce4-session 40 manual mode Press <enter> to keep the current choice[*], or type selection number:
输入 3 以启动 Xfce4,回显如下:
root@kali:~# update-alternatives --config x-session-manager There are 3 choices for the alternative x-session-manager (providing /usr/bin/x-session-manager). Selection Path Priority Status ------------------------------------------------------------ * 0 /usr/bin/gnome-session 50 auto mode 1 /usr/bin/gnome-session 50 manual mode 2 /usr/bin/startxfce4 50 manual mode 3 /usr/bin/xfce4-session 40 manual mode Press <enter> to keep the current choice[*], or type selection number: 3 update-alternatives: using /usr/bin/xfce4-session to provide /usr/bin/x-session-manager (x-session-manager) in manual mode
卸载 Gnome 桌面环境:
apt remove gnome-core apt remove gnome-shell
重启系统:
reboot
重新登录系统之后可以看到已经成功地将 Kali Linux 的桌面环境更换为 Xfce 4,如图 2:
探秘维基解密网站的服务器和域名
2019 年 04 月 11 日,维基解密的创始人朱利安·阿桑奇因为失去了厄瓜多尔政府的政治庇护,在位于伦敦的厄瓜多尔驻英国大使馆中被英国警方逮捕。

维基解密网站成立于 2006 年 12 月,至今该网站仍然在运作并可以通过国际互联网访问。

于是我就在想,维基解密使用的服务器在哪里?域名如何解析的?
带着这些疑问,我使用一台位于国外的 VPS, Ping 了一下 “wikileaks.org” 这个域名,测试结果如下:
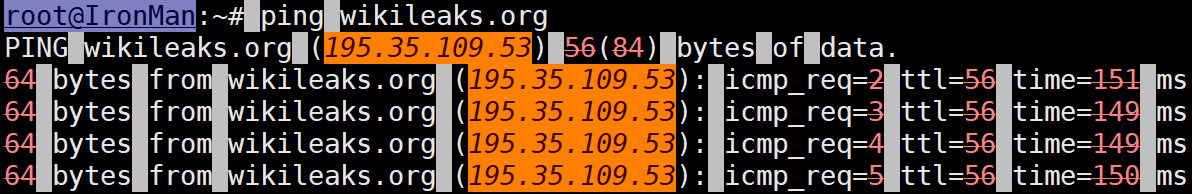
由图 4 可知,解析到的 “wikileaks.org” 这个域名所在的服务器的 IP 地址是 ”195.35.109.53”.
随后,我在 Ipinfo(https://ipinfo.io/) 这个网站查询了 “195.35.109.53” 这个 IP 的信息(https://ipinfo.io/195.35.109.53),查询结果如图:
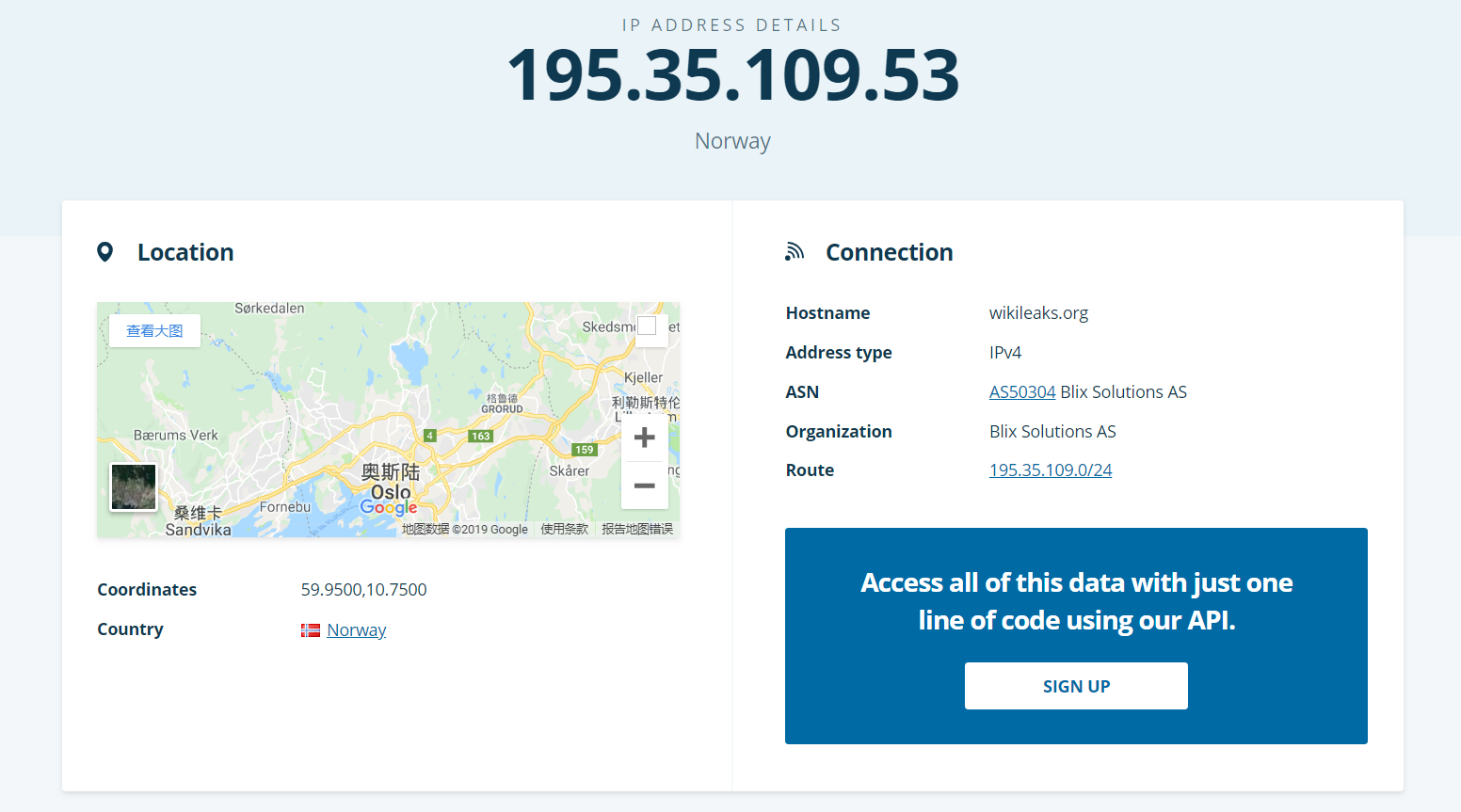
根据查询结果显示, “195.35.109.53” 这个 IP 地址的托管机构是位于挪威奥斯陆的 Blix Solutions AS.
Blix Solutions AS 的官网首页如图:
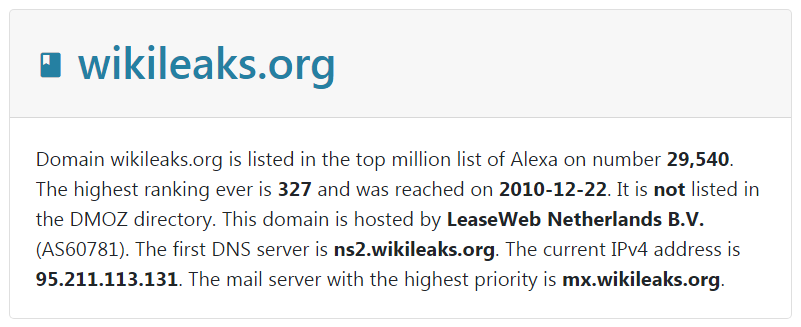
在 “dnslytics.com” 上查询 “wikileaks.org” 可以获得如下信息(https://dnslytics.com/domain/wikileaks.org):
域名 “wikileaks.org” 的基础信息:
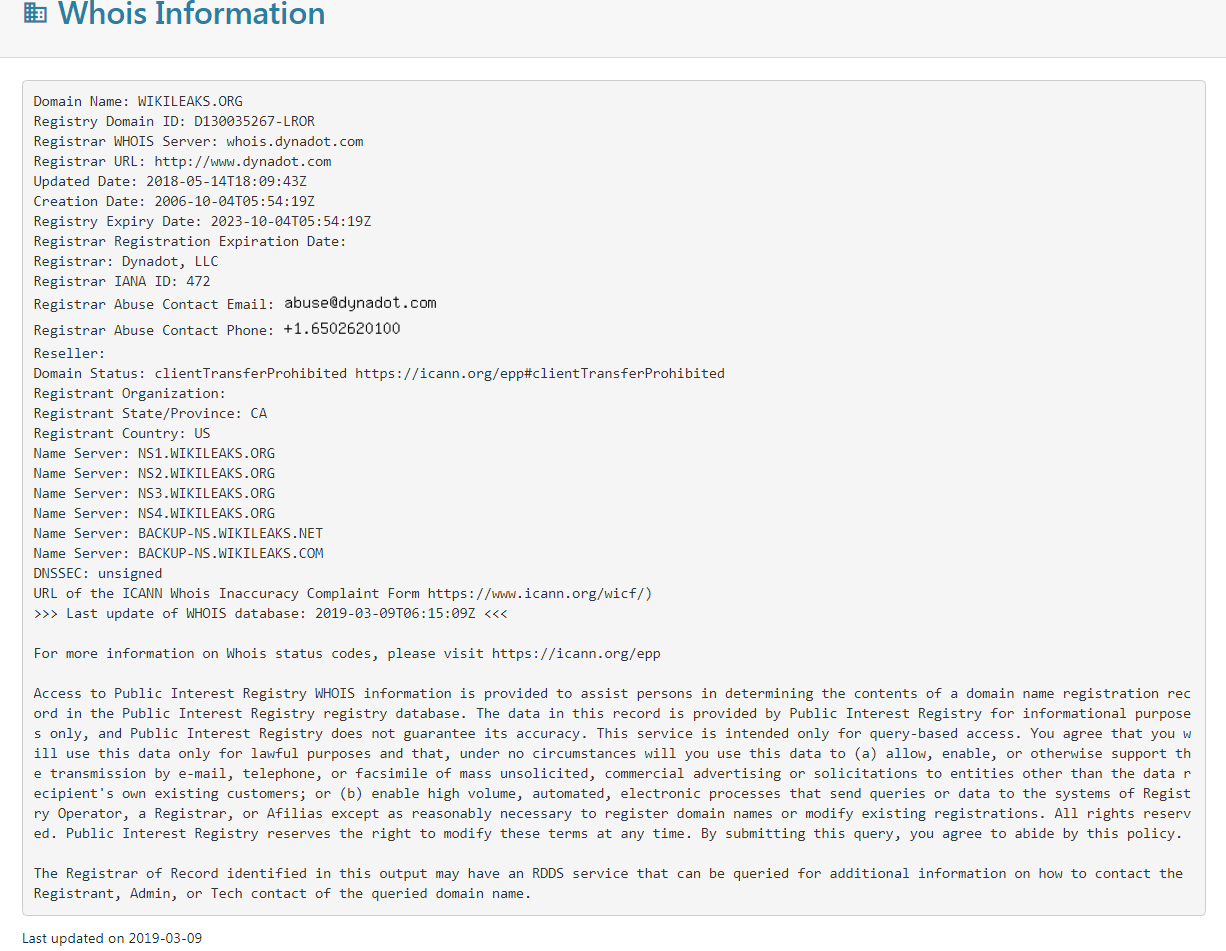
Whois 信息:
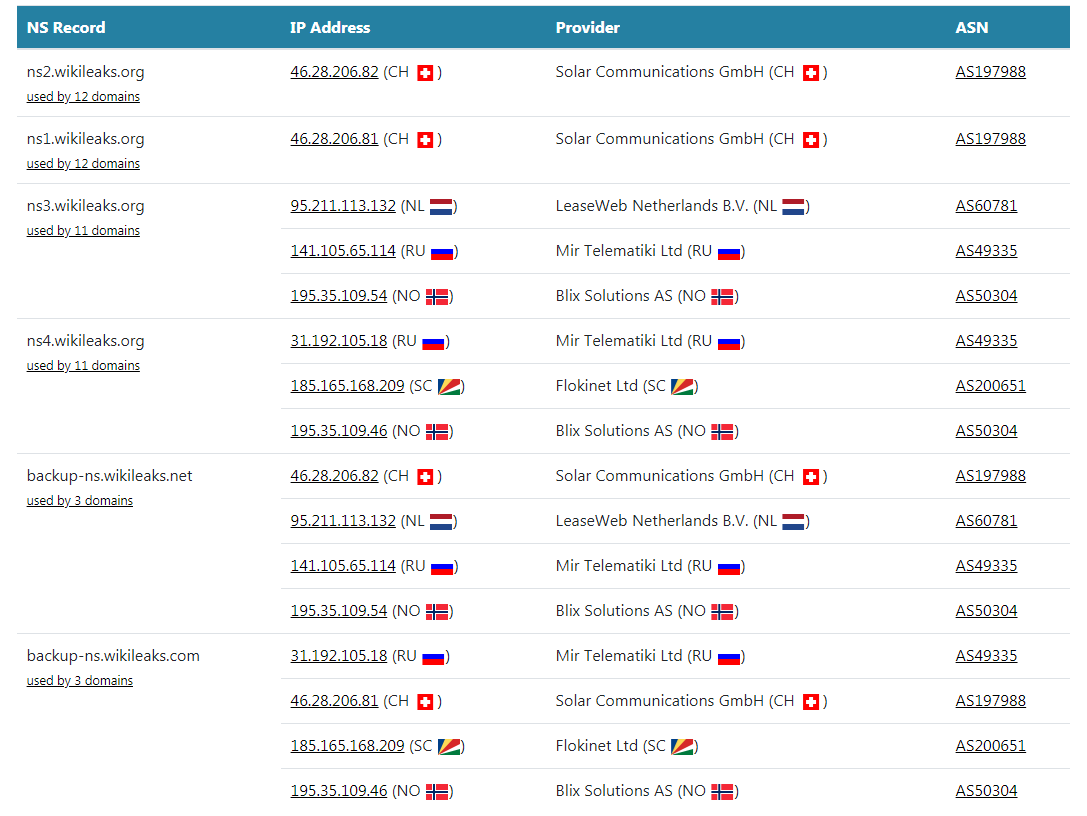
NS 记录:
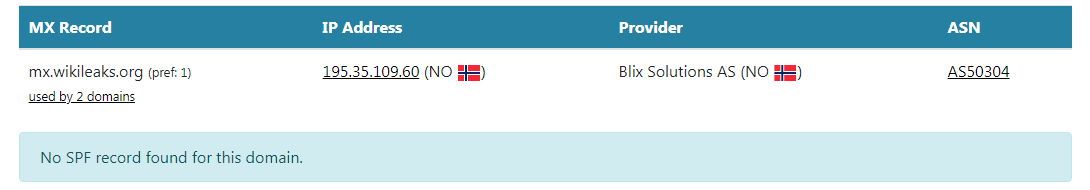
MX 记录:
在 dnslytics.com 上查询 IP 地址 “195.35.109.53” 可以看到(https://dnslytics.com/ip/195.35.109.53), 该 IP 地址和域名 “wikileaks.org” 之间的 DNS 解析服务由 “host1.no” 提供,HOST1 是一家位于挪威奥斯陆的网络公司,提供虚拟主机,云服务器和域名购买服务等,其官网首页如图:
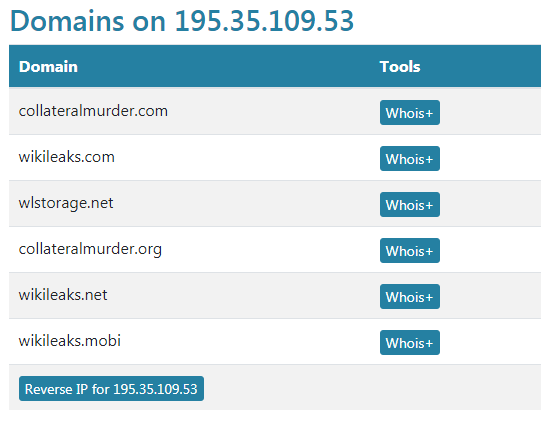
此外,我们在 dnslytics.com 提供的查询结果中还可以看到,有 6 个域名都解析到了IP 地址为 “195.35.109.53” 的这台服务器上,这些域名应该都是属于维基解密的。
在中文维基百科中可以找到如下关于维基解密网站所使用的主机和域名的信息:
主机
维基解密形容自己为“一个对大量来源不明的泄密文件进行审查的系统”。该网址可被多个服务器使用且不同的域名伴随着大量的阻断服务攻击,同时它的切断服务来自不同的域名解析系统提供者。
直到2010年8月,维基解密一直使用PRQ的主机,一个提供“高度安全性,零故障的主机服务”的瑞典公司。据说PRQ公司“几乎没有关于其客户的信息,很少进行维护”。维基解密网站托管在以坚持客户匿名著称的瑞典网络服务提供商PRQ.se,这家公司可以承受法律压力和网络攻击。先将文件送到位于比利时的服务器上,再送到位于“另一个法律上较友善的国家”的服务器上,然后这些文件被转存到其他地方后删除,。由一批匿名的工程师提供技术维护,整个流程和提交的文件都被加密,并使用经过修改的Tor网络匿名传输,整个系统即使核心成员也无法全部进入。此外,维基解密还在系统中一直传递许多虚假的提交文件,以使真正的文件难以被发现。
现在,维基解密的主机主要由建在一座核掩体中的Bahnhof公司提供。其他服务器以瑞典服务器为中心分布于全世界。阿桑奇曾说服务器设置在瑞典(及其他国家)“主要是因为这些国家能为这个网站的泄密行为提供法律保护”。他认为瑞典宪法给予了那些信息提供者完全的法律保护。在瑞典,政府对任何类型的报纸的消息来源的问询都是被禁止的。这些法律,以及PRQ的主机,让任何一个政府迫使维基解密下线的行动都变得困难,它们设置了一个能抵御来自任何牢骚者的诉讼的保护伞,保护了维基解密的自由。维基解密在秘密地点维护他们的服务器、删除服务器日志并使用军事级别的加密技术来保护信息源和其它机要信息。”该种服务器组织形式被称为“防弹主机”。
2010年8月17日,一则消息被宣布,瑞典海盗湾将提供并管理多台维基解密的新服务器。海盗湾捐赠了免费的服务器和宽带给维基解密。该机构技术员将保证这些服务器的维护和工作。
在这个放置在旧服务器上的地址变成一个黑客拒绝式服务攻击的目标后,维基解密把其地址移到了亚马逊的服务器上。然而随后不久,该网址在亚马逊服务器上被“废止”。在一份公开声明中,亚马逊说维基解密未遵守它的服务条款。公司进一步解释说,“它们违反了条款的几个部分。比如,我们的服务条款声明‘你显示或授权显示的内容,不能用于支持违法或者可能导致某人或法律实体受到伤害的行为。’显然,维基解密显示了这种内容。”之后维基解密决定安装由法国OVH公司提供的属于维基解密自己的服务器。在受到来自法国政府的批评人士的刁难后,该公司转于寻求两个法院进行针对为维基解密提供服务器案的裁决。当里尔的法院迅速倾向于迫使OVH关闭维基解密网站时,巴黎法院声明他们需要更多的时间来研究高技术议题。
维基解密建立在几个软件包的基础上,包括Tor, PGP, MediaWiki以及Freenet。维基解密积极鼓励通过Tor发送信息,因为它能满足用户强烈的保密需求。
2010年11月4日,阿桑奇告诉瑞士电视台TSR他急需在中立的瑞士寻求政治庇护并建立一个维基解密基金以把各种工作移到这里。按阿桑奇所言,瑞士和冰岛是仅有的几个能让维基解密感到可以安全地工作的国家。
域名服务器
维基解密曾经使用EveryDNS的域名解析服务,该域名服务器曾受到DDoS攻击。攻击影响了EveryDNS的服务质量,故而该公司撤除了对维基解密的服务。资深的维基解密支持者通过一次DDoS攻击报复了EveryDNS。此外,由于博客中的错误,一些支持者误将EasyDNS当做EveryDNS,随后数量可观的支持者参与了对EasyDNS的抵制,最终迫使EasyDNS决定提供域名解析服务给维基解密。
https://zh.wikipedia.org/wiki/維基解密
根据上面的信息,维基解密曾使用过 PRQ 公司提供的主机服务,我搜索了一下,确实存在一个使用了 “PRQ.se” 域名并且经营主机服务的公司,其官网首页如图:
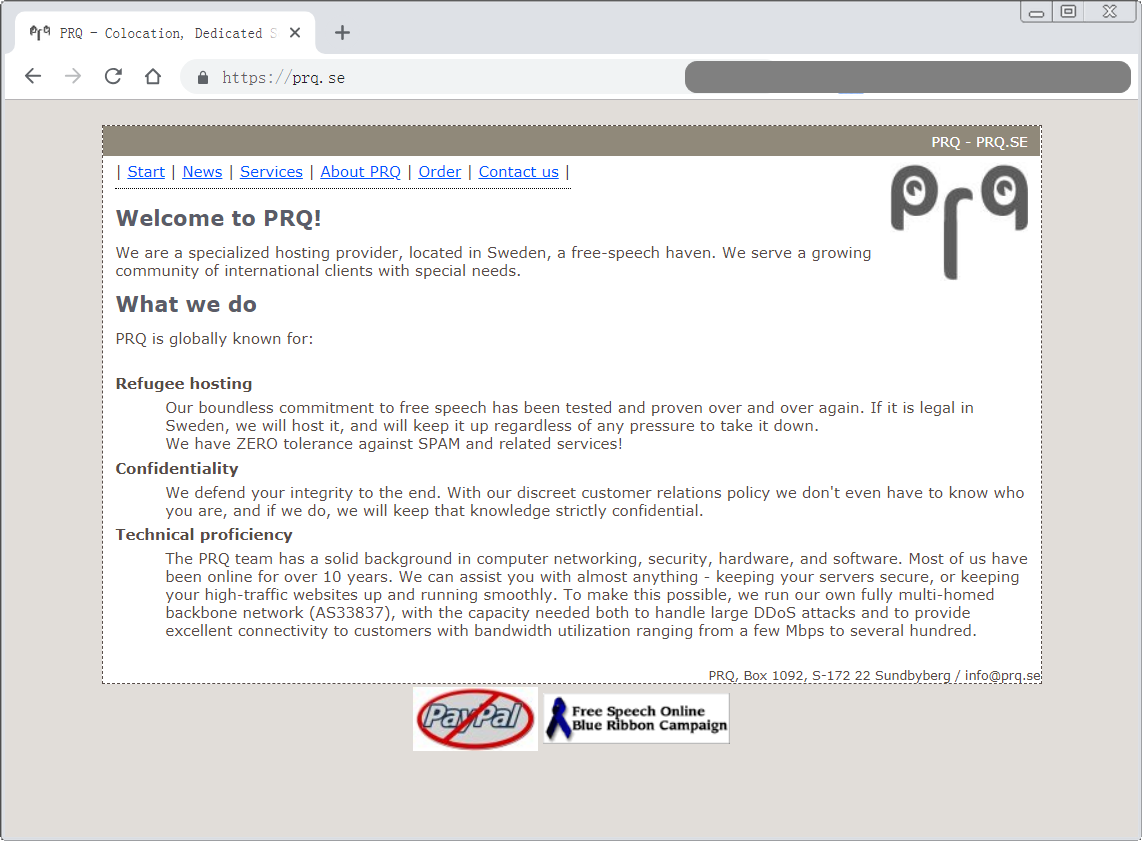
今天的探秘就到这里了。说是“探秘”其实也不准确,因为上面这些信息都是公开的,不过我之前确实不知道这些信息,所以我了解了一些之后就把我查到的资料放在这里与大家分享一下,满足一下小小的好(偷)奇(窥)心(欲)。